Calculator and formulas for calculating the voltage and power of an RC series circuit
This function calculates the voltages, powers, currents, impedance and reactance of a series circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor.
|
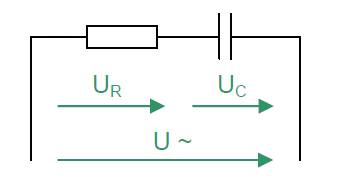
The total resistance of the RC series circuit in the AC circuit is called Impedance Z. Ohm's law applies to the entire circuit.
The current is the same at every measuring point. Current and voltage are in phase at the ohmic resistance. The voltage rushes across the capacitive reactance of the capacitor after the current by −90 °.
The total voltage U is the sum of the geometrically added partial voltages. For this purpose, both partial voltages form the legs of a right triangle. Its hypotenuse corresponds to the total voltage U. The resulting triangle is called the voltage triangle or vector diagram of the voltages.
\(\displaystyle U=\sqrt{{U_R}^2+{U_C}^2} \) \(\displaystyle φ=arctan \left( \frac{U_C}{U_R} \right) \)
\(\displaystyle U\) Total voltage \(\displaystyle U_R\) Voltage across the resistor \(\displaystyle U_C\) Voltage across the capacitor
\(\displaystyle Z=\sqrt{R^2+{X_C}^2} \)
\(\displaystyle R\) Real power \(\displaystyle X_C\) Reactance \(\displaystyle Z\) Impedance
\(\displaystyle S=\sqrt{P^2+Q^2} \) \(\displaystyle φ=arctan \left( \frac{Q}{P} \right) \)
\(\displaystyle P\) Real power \(\displaystyle Q\) Reactive power \(\displaystyle S\) Apparent power
The multiplication of the instantaneous values of voltage U and current I results in the power curve.
The multiplication of the voltage across the resistor and the current result in the real power. The real power is converted into heat in the resistor.
\(\displaystyle P=U_R·I \) \(\displaystyle P=R·I^2 \)
The reactive power oscillates back and forth between the capacitor and the generator.
\(\displaystyle Q=U_C ·I \) \(\displaystyle Q=X_C ·I^2 \)
The apparent power is a purely arithmetic variable.
\(\displaystyle S=U ·I \) \(\displaystyle S=Z ·I^2 \)
The power factor indicates how much of the apparent power S is the real power P is generated.
\(\displaystyle cos(φ)=\frac{P}{S} \)
\(\displaystyle S\) Apparent power \(\displaystyle P\) Real power \(\displaystyle φ\) Phase shift
|
|