Ammeter Shunt Resistor
Calculator and formulas for calculating the shunt resistor for measuring range extension
Shunt Resistor Calculator
Measuring Range Extension
Calculation of the shunt resistor to extend the measuring range of an ammeter. Choose between meter resistance or total voltage as input parameter.
Ammeter Shunt Resistor
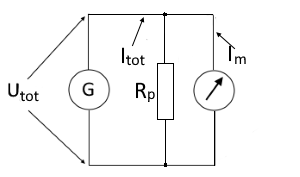
Circuit diagram: Ammeter with shunt resistor
Purpose of Shunt Resistor
- Measuring range extension for ammeters
- Current division to protect the meter movement
- Enables measurement of larger currents
- Prevents overload of the measuring device
Input Modes
Important Note
Formulas for Shunt Resistor Calculation
Main Formula via Meter Resistance
With the ratio n = Itotal / Im:
Current ratio determines shunt resistor
Total Resistance
Parallel connection of meter and shunt:
Conductances are added
Power Calculation
The power dissipation in the shunt resistor must be considered in the design:
Practical Calculation Example
Example: Measuring range extension from 2A to 20A
Given: Meter movement with Rm = 10Ω, measuring range 2A to be extended to 20A
Step 1: Calculate current ratio
Step 2: Calculate shunt resistor
Step 3: Verify current distribution
Through shunt: Is = 20A - 2A = 18A
Step 4: Shunt power
Theory and Practical Applications
Operating Principle
In an ammeter, shunt resistors are used to extend the measuring range. The shunt resistor is connected in parallel with the measuring device to divide the current. This way, only a small portion of the total current flows through the sensitive meter movement.
Important Properties
- Current division: Current divides inversely proportional to the resistances
- Same voltage: Meter movement and shunt have the same voltage
- Precision: Shunt resistors must be very accurate
- Stability: Use temperature-stable materials
Practical Applications
- Digital multimeters: Current measurement in different ranges
- Industrial measurement technology: High current monitoring
- Energy measurement: Current transformers in energy meters
- Battery management: Charging current monitoring
Symbol Directory
| Utotal | Total voltage = meter movement voltage |
| Itotal | Total current |
| Im | Current in meter movement |
| Rm | Resistance of meter movement |
| Rs | Value of shunt resistor |
| Ps | Power/load capacity of shunt resistor |
Important Notes
- Shunt resistor must be precisely dimensioned
- Consider power handling of shunt
- Account for temperature coefficient
- Minimize contact resistances
- Calibration after installation
Practical Tips
- Manganin or Constantan as shunt material
- Kelvin connection for precise measurement
- Heat dissipation for high currents
- Protection from mechanical stress
- Regular calibration