Calculate Bessel-Je Function
Online calculator for the exponentially scaled Bessel function Jeᵥ(z) of the first kind - Numerically stable oscillating cylindrical function
Bessel-Je Function Calculator
Exponentially Scaled Bessel Function
The Jeᵥ(z) or exponentially scaled Bessel function shows stable oscillating behavior as a cylindrical function.
Bessel-Je Function Curve
Mouse pointer on the graph shows the values.
The exponentially scaled form eliminates amplitude growth for large z.
Why oscillating behavior instead of exponential growth?
The standard Bessel function differs fundamentally from modified Bessel functions:
- Periodic oscillation: Jᵥ(z) oscillates for large z
- Damping amplitude: Amplitude ~ 1/√z
- Physical waves: Describes vibration and wave processes
- Cylindrical symmetry: Solutions in cylindrical coordinates
- Zeros: Infinitely many zeros for large z
- Asymptotics: Jᵥ(z) ~ √(2/πz) cos(z - πν/2 - π/4)
Applications in wave problems and cylindrical symmetry
The Bessel-Je function is the numerically stable solution for oscillating wave processes:
Mechanical Vibrations
- Circular membrane vibrations
- Cylinder and tube vibrations
- Acoustic resonators
Electromagnetic Waves
- Cylindrical waveguides
- Antenna radiation
- Cavity resonators
Formulas for the Bessel-Je Function
Definition
Exponentially scaled Bessel function
Relationship to Jᵥ
Inversion of scaling
Series Expansion
Scaled power series
Asymptotic Form
For large z (with stable amplitude)
Recurrence Formula
Same recurrence as unscaled version
Integral Representation
For integer order n
Special Values
Important Values
Symmetry Properties
For integer n
Behavior at z = 0
Same behavior as Jᵥ(0)
Application Areas
Wave propagation, vibration problems, cylindrical geometry, antenna design.
Bessel-Je Oscillation Pattern
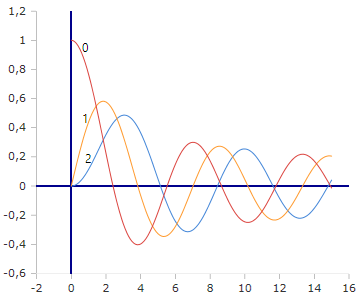
Bessel-Je Functions (Order 0,1,2)
The exponentially scaled functions show clear oscillations with controlled amplitude without numerical instabilities.
Characteristic Properties
- Je₀(z) starts at 1, then oscillates
- Jeₙ(z) with n > 0 starts at 0
- Asymptotically: ~ √(2/πz) cos(...)
- Stable amplitude through scaling
Detailed Description of the Bessel-Je Function
Mathematical Definition
The exponentially scaled Bessel function Jeᵥ(z) is a numerically stabilized version of the standard Bessel function Jᵥ(z). Unlike modified Bessel functions, it retains the oscillating behavior but eliminates numerical instabilities.
Using the Calculator
Enter the order ν (integer) and the argument z (positive real number). The graph stretch parameter controls the X-axis scaling for better visualization.
Physical Background
Bessel functions were originally developed by Friedrich Bessel for astronomical calculations. They describe wave propagation in cylindrical systems and are fundamental to many physical phenomena.
Properties and Applications
Physical Applications
- Circular membrane vibrations (drum head)
- Electromagnetic waves in cylindrical conductors
- Acoustic resonators and cavities
- Diffraction at cylindrical objects
Mathematical Properties
- Oscillating behavior for large z
- Damping amplitude ~ 1/√z
- Symmetry: Je₋ₙ(z) = (-1)ⁿ Jeₙ(z) for integer n
- Infinitely many zeros for z > 0
Numerical Aspects
- Stability: Numerically stable for complex arguments
- Scaling: Eliminates exponential growth for Im(z) ≠ 0
- Accuracy: Maintained precision in all z ranges
- Efficiency: Optimized algorithms available
Interesting Facts
- Bessel functions describe the vibration modes of drums
- The zeros of J₀(z) determine resonance frequencies of cylindrical cavities
- Bessel functions are essential for the Fourier-Bessel transform
- They appear in quantum mechanics for radially symmetric problems
Calculation Examples and Oscillation Properties
Small Argument
z = π/2:
J₀(π/2) ≈ 0.567
Je₀(π/2) ≈ 0.567
First Zero
z ≈ 2.405:
J₀(2.405) ≈ 0
Je₀(2.405) ≈ 0
Large Argument
z = 20:
J₀(20) ≈ 0.167
Je₀(20) ≈ 0.167
Wave Applications and Cylindrical Symmetry
Acoustic Applications
Drum head vibrations:
Radial modes: u(r,φ,t) = J₀(k·r) cos(ωt)
Zeros determine resonance frequencies
Example: Circular membrane with radius R has resonances at k·R = zeros of J₀.
Electromagnetic Waves
Cylindrical waveguides:
TM modes: E_z ∝ J_m(k_c·r) e^(imφ)
Cutoff frequencies through Bessel zeros
Example: TE₀₁ mode in waveguide has lowest cutoff frequency.
Zeros and Oscillation Behavior
Important Zeros
J₀(z) zeros:
2.405, 5.520, 8.654, 11.792, ...
J₁(z) zeros:
3.832, 7.016, 10.173, 13.324, ...
Asymptotics: Zeros follow αₙ ≈ (n - 1/2)π for large n.
Oscillation Properties
Asymptotic behavior:
Jᵥ(z) ~ √(2/πz) cos(z - νπ/2 - π/4)
Period ≈ 2π, amplitude ~ 1/√z
Properties: Oscillation frequency remains constant, only amplitude decreases.
Numerical Computation and Algorithms
Computation Methods
- Series Expansion: For small |z| and small ν
- Asymptotic Expansion: For large |z|
- Recurrence Relations: For adjacent orders
- Continued Fractions: For special ranges
Software Implementations
- GNU GSL: Highly accurate implementations
- Boost Math: C++ template library
- SciPy: Python scipy.special.jn
- MATLAB: Built-in besselj function
|
|