Online trapezoid calculator
Online calculator and formulas for trapezoid computations
Trapezoid Calculator
Trapezoid calculation
To compute the trapezoid provide either the parallel sides a and c, height h and excess x; alternatively supply a angle and three side lengths.
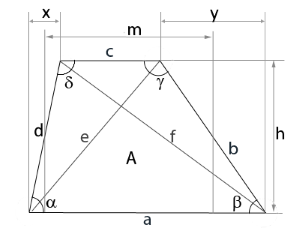
Trapezoid diagram
The diagram shows a general trapezoid with all parameters.
Computations are performed using different combinations of sides, angles and height.
Calculation methods for the trapezoid
The trapezoid calculator offers several calculation methods depending on available parameters:
- Excess method: sides a, c, height h and excess x
- Angle α/δ method: three sides and angle α or δ
- Angle β/γ method: three sides and angle β or γ
- Automatic computation: All missing parameters are calculated
- Complete results: sides, angles, area, perimeter, diagonals
- Accurate formulas: trigonometric and geometric calculations
Formulas for the trapezoid
Side lengths
Basic side calculations
Area and perimeter
Area and perimeter calculations
Angles
Angle relationships in the trapezoid
Diagonals and excesses
Diagonals and horizontal excesses
Calculation example
Given (excess method)
Find: All parameters of the trapezoid
1. Compute legs
Calculation of the slanted sides
2. Area and perimeter
Area and perimeter calculation
3. Compute angles
All four angles of the trapezoid
4. Diagonals
All geometric parameters determined
Practical applications of trapezoid calculations
General trapezoid calculations are applied across many technical and scientific fields:
Construction & Architecture
- Roof structures with variable slopes
- Foundation cross-sections and slopes
- Bridge piers and retaining walls
- Stair runs and ramps
Engineering & Production
- Flow channels with trapezoidal cross-sections
- Tool profiles and cutting edges
- Gear wheels and V-belt profiles
- Containers and hopper designs
The trapezoid in geometry
The general trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. This universal calculator enables computing all geometric parameters based on different input combinations. The flexible calculation methods make it a valuable tool for technical and scientific applications.
Computations can be performed either via the excess method (when height and horizontal offset are known) or via angle methods (when angles and three side lengths are known). All results are computed automatically and include side lengths, angles, area, perimeter, diagonals and excesses.
For specialized tasks there are additional trapezoid calculators available, optimized for specific trapezoid types (symmetric, right-angled) or dedicated calculations (area only, angles only).
|
|