Calculate Irregular Octagon
Calculator and formulas for the elongated octagon
Irregular Octagon Calculator
The irregular octagon
An irregular octagon is an elongated octagon with two different side lengths but equal interior angles of 135°.
Octagon structure
The irregular octagon has two different side lengths.
All interior angles are uniformly 135°.
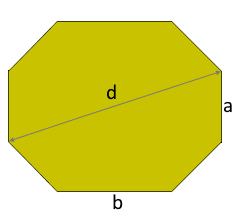
The irregular elongated octagon
The irregular octagon is a special form of octagon with unique properties:
- Eight sides: 6 sides of length a, 2 sides of length b
- Equal angles: All interior angles are 135°
- Elongated form: Rectangular middle part with beveled corners
- Simple calculation: Only two parameters required
- Practical form: Common in technical applications
- √2 relationships: Mathematically elegant proportions
Angle properties
The angle structure of the irregular octagon is remarkably uniform:
Interior angles
- All 8 interior angles = 135°
- Sum: 8 × 135° = 1080°
- Matches octagon formula: (8-2) × 180°
- 45° more than right angle
Exterior angles
- All 8 exterior angles = 45°
- Sum: 8 × 45° = 360°
- Matches general polygon rule
- Half right angle per corner
Geometric structure analysis
The geometric structure of the elongated octagon:
Construction principle
- Middle part: Rectangle of size (b-a) × h
- Side parts: 2 squares of size a × a
- Corners: 4 beveled 45° triangles
- Symmetry: Horizontally and vertically symmetric
√2 mathematics
- Height: h = a(1 + √2)
- Length: l = a(1 + √2) + b - a
- √2 ≈ 1.414: Fundamental for 45° geometry
- Elegant formulas: Minimal complexity
Applications of the irregular octagon
The elongated octagon finds diverse practical applications:
Mechanical engineering & technology
- Special tool profiles
- Pipeline cross-sections
- Gear and cam forms
- Structural hollow profiles
Architecture & construction
- Window and door openings
- Column and pillar profiles
- Decorative wall elements
- Pavilion and gazebo floor plans
Design & art
- Furniture design and tabletops
- Logo design and symbols
- Jewelry and decorative objects
- Textile patterns and ornaments
Traffic & infrastructure
- Road signs and traffic signs
- Tunnel and bridge profiles
- Parking lot and area markings
- Guard rails and barriers
Formulas for the irregular octagon
Length l
Total length of the elongated octagon
Height h
Height based only on short side a
Perimeter P
6 short sides plus 2 long sides
Diagonal d
Pythagorean theorem applied to length and height
Area A
Composed of squares, triangles and rectangle
√2 constant
Fundamental for 45° angle geometry
Interior angles
All interior angles are equal
Calculation example for an irregular octagon
Given
Find: All geometric properties of the elongated octagon
1. Calculate basic dimensions
Height and total length
2. Perimeter and diagonal
Total perimeter and main diagonal
3. Area calculation
Composition from different geometric elements
4. Complete irregular octagon
The complete elongated octagon - practical form with elegant mathematics
The irregular octagon: Practical geometry
The irregular elongated octagon is a fascinating example of how practical requirements can lead to elegant geometric solutions. As an octagon with two different side lengths but uniform interior angles, it combines the simplicity of regular forms with the flexibility of irregular constructions, finding broad application in technology and design.
Geometric elegance despite irregularity
The special feature of the elongated octagon lies in its structural clarity:
- Uniform angles: All 8 interior angles are exactly 135°
- Two side lengths: 6 short sides (a) and 2 long sides (b)
- √2 mathematics: All relationships based on √2 ≈ 1.414
- Modular construction: Rectangular middle part with beveled ends
- Symmetric structure: Horizontally and vertically mirror-symmetric
- Simple formulas: Despite irregularity, mathematically manageable
The 135° angle: Geometric perfection
The uniform interior angle of 135° makes this octagon special:
Mathematical significance
135° = 90° + 45°, the perfect combination of right angle and 45° bevel. This enables both orthogonal and diagonal construction elements.
Constructive advantages
The 135° angle allows clean transitions between horizontal/vertical and diagonal elements, ideal for manufacturing and assembly processes.
Aesthetic harmony
The 45° bevels (exterior angles) create visual dynamism while uniform angles provide calm and order.
Practical application
Standard tools and machines can easily execute 45° cuts, simplifying manufacturing and reducing costs.
Versatile practical applications
The elongated octagon finds application in many areas:
- Mechanical engineering: Profiles for shafts, pipes and structural components
- Architecture: Columns, pillars and decorative elements
- Traffic engineering: Signs, markings and guardrail profiles
- Furniture design: Tabletops, frames and functional elements
- Electronics: Housing and heat sink profiles
- Optics: Lens and prism forms for special applications
Mathematical considerations and optimization
The mathematical structure enables interesting optimization approaches:
Area optimization
For a given perimeter, the ratio a:b can be chosen so that the area is maximized or optimized for special requirements.
Material efficiency
The simple formulas allow precise material requirement calculation and waste optimization in industrial manufacturing.
Structural analysis
The uniform angles simplify stress analysis and enable precise predictions about load capacity and deformation.
Manufacturing aspects
Reduction to only two parameters (a and b) significantly simplifies design, manufacturing and quality control.
Summary
The irregular elongated octagon exemplifies how mathematical elegance and practical applicability can go hand in hand. Its apparent irregularity conceals a deep geometric order: The uniform 135° angles create structural clarity while the two different side lengths provide the necessary flexibility for diverse applications. From √2-based mathematics to industrial manufacturing, this form demonstrates that true geometric beauty does not lie in perfect regularity, but in the intelligent balance between order and adaptability. In a world that demands both efficiency and versatility, the elongated octagon offers an optimal solution - mathematically well-thought-out, technically feasible and aesthetically appealing.
|
|